
Knee Meniscal Tears
Mechanism of Knee Meniscal Tears
Knee meniscal tears can occur due to various mechanisms, including traumatic injuries and degenerative changes. Here are some common mechanisms of knee meniscal tears:
1. Twisting or Rotational Forces:
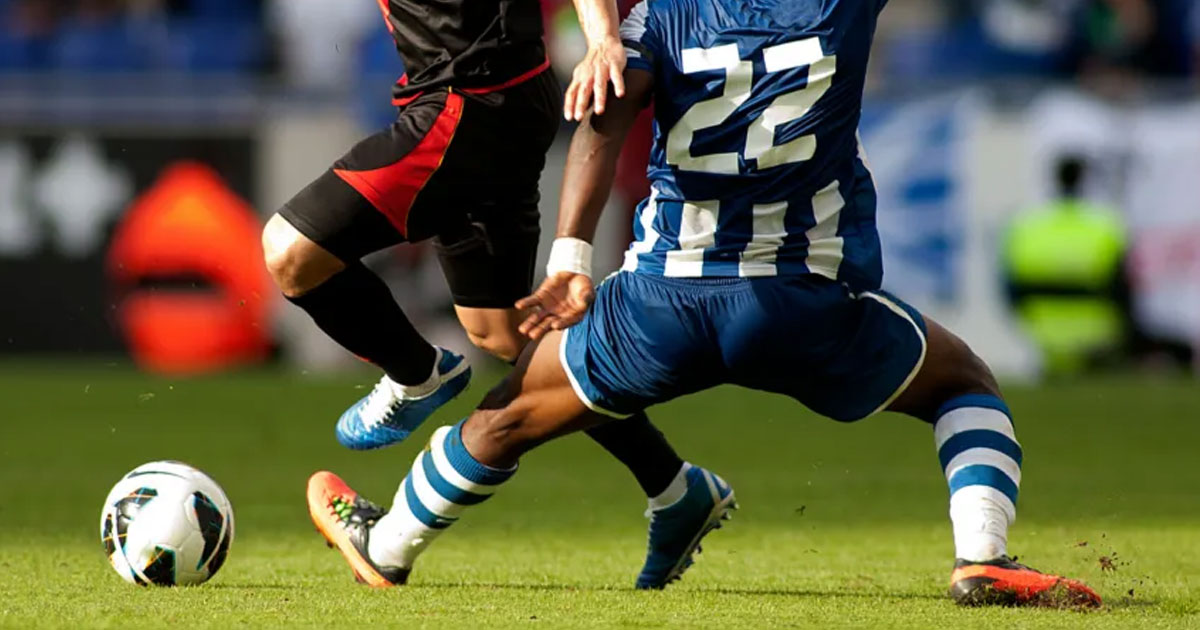
- One of the most common mechanisms of acute meniscal tears is a twisting or rotational force applied to the knee joint while the foot is fixed on the ground.
- This can occur during sports activities such as soccer, basketball, skiing, or football, especially when sudden pivoting or changes in direction occur.
2. Sudden Impact or Direct Trauma:
- Meniscal tears can also occur as a result of a direct blow to the knee, such as a tackle in football or a collision in basketball.
- The impact force can compress and shear the meniscus, causing tears in its tissue.
3. Hyperflexion or Hyperextension:
- Extreme flexion or extension of the knee joint beyond its normal range of motion can also lead to meniscal tears.
- This can happen during falls or accidents where the knee is forcefully bent or straightened beyond its limits.
4. Weight-Bearing with Rotation:
- Weight-bearing combined with rotational movements of the knee, such as squatting and twisting simultaneously, can put stress on the meniscus and lead to tears.
- Activities that involve repetitive loading of the knee joint with rotational components, such as cutting manoeuvres in sports, can also contribute to meniscal injuries over time.
5. Degenerative Changes:
- In older individuals, meniscal tears can result from degenerative changes in the meniscus over time.
- The meniscus becomes less elastic and more prone to tears with age, and tears may develop gradually as a result of wear and tear on the knee joint.
6. Chronic Overuse or Repetitive Stress:
- Chronic overuse or repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as repetitive squatting, kneeling, or lifting heavy loads, can contribute to the development of meniscal tears, especially in individuals involved in occupations or activities that place repeated stress on the knees.
Types of Meniscal Tears
Meniscal tears can vary in their location, pattern, and severity. Here are some common types of meniscal tears:
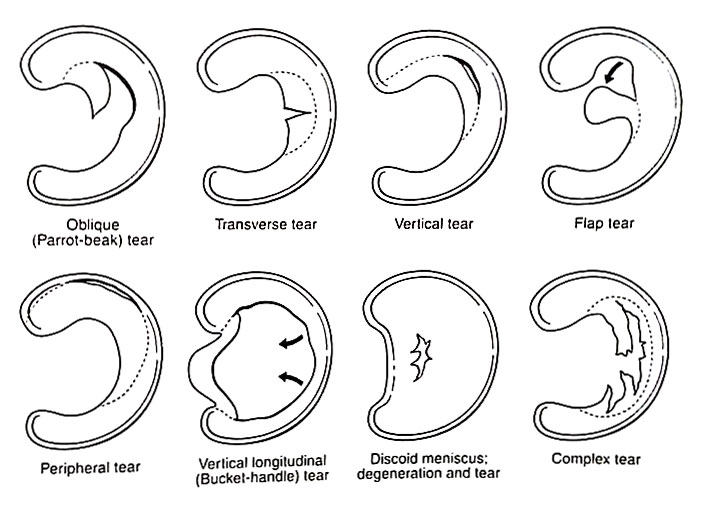
1. Radial Tear:
- Radial tears occur perpendicular to the circumferential fibres of the meniscus.
- They can be further classified into vertical, horizontal, or oblique radial tears depending on their orientation.
- Radial tears often extend from the inner edge of the meniscus to the outer edge.
2. Longitudinal Tear:
- Longitudinal tears run parallel to the circumferential fibres of the meniscus.
- These tears can be partial or complete and may extend into other types of tears, such as radial tears.
3. Bucket Handle Tear:
- Bucket handle tears are a type of longitudinal tear where a portion of the meniscus detaches and flips into the joint space, resembling the handle of a bucket.
- This type of tear can cause mechanical symptoms like locking or catching of the knee joint.
4. Flap Tear:
- Flap tears involve a portion of the meniscus tearing away from the main body, creating a flap-like structure.
- Flap tears can also cause mechanical symptoms and may interfere with normal knee function.
5. Degenerative Tear:
- Degenerative tears are associated with age-related changes in the meniscus, such as weakening and fraying of the tissue.
- These tears often occur in older individuals and may not be associated with a specific injury.
6. Complex Tear:
- Complex tears involve a combination of different tear patterns, such as radial and longitudinal tears occurring simultaneously.
- These tears can vary widely in their presentation and may require careful assessment and treatment planning.
7. Peripheral Tear:
- Peripheral tears occur in the outer region of the meniscus, where blood supply is relatively better compared to the inner region.
- Peripheral tears may have a better potential for healing compared to tears in the inner (avascular) region of the meniscus.
8. Root Tear:
- Root tears involve detachment or avulsion of the meniscal root from its attachment site on the tibia.
- These tears can disrupt the normal function of the meniscus and may lead to instability and degenerative changes in the knee joint.
The type of meniscal tear, along with factors such as the location, size, and stability of the tear, will influence the choice of treatment, which may range from conservative management with physical therapy to surgical intervention such as arthroscopic meniscal repair or partial meniscectomy.
Treatment of Meniscal Tears
Treatment and rehabilitation for knee meniscal injuries depend on several factors, including the severity and location of the tear, the patient's age, activity level, and overall health. Here's an overview of common approaches:
1. Conservative Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the symptoms and allow the knee to heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling.
- Compression: Use compression bandages or braces to support the knee and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevate the leg to reduce swelling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Physiotherapy:
- At Sports and Spines Physiotherapy we can provide a safe structured rehabilitation programme to improve knee strength, flexibility, and stability (proprioception).
- Exercises may include range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee (especially the quadriceps and hamstrings), and balance and proprioception training.
- Manual therapy techniques such as massage and joint mobilization may also be used to improve knee function.

Physiotherapy exercises for balance and proprioception training are an important part of the treatment of meniscal tears
3. Injection Therapy:
- Corticosteroid injections: These can be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, particularly in cases of acute flare-ups.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections: PRP injections may promote healing by delivering growth factors to the injured tissue.
- Hyaluronic acid injections: These injections can help lubricate the knee joint and reduce pain.
4. Surgical Treatment:
- Arthroscopic surgery: In cases where conservative treatment fails or for more severe meniscal tears, arthroscopic surgery may be recommended.
- Depending on the nature of the tear, the surgeon may perform a meniscectomy (removal of the torn portion of the meniscus) or a meniscus repair (suturing the torn edges together).
- Rehabilitation following surgery typically involves a gradual progression of exercises to regain strength, flexibility, and function in the knee.
5. Rehabilitation Guidelines:
- Initially, focus on reducing pain and swelling, restoring range of motion, and regaining muscle strength.
- Progress to more advanced exercises targeting functional activities, proprioception, and agility.
- Return to sport or physical activity should be gradual, with close monitoring of symptoms and progression guided by a physiotherapist.
Rehabilitation for knee meniscal injuries is typically individualized based on the specific characteristics of the injury and the patient's goals and needs. At Sports and Spines Physio we have had great outcomes with post-surgery meniscal repairs and clients who have had meniscal injuries that have not required surgery.
